2022-07-02

INTRODUCTION:
1. The development of the normal placenta.
Placenta, an important connection between the uterus of the mother and the stomach of the fetus. It helps in nourishment, development, excretion and gaseous exchange in fetus trough blood circulation of mother.
The development of placenta starts when blastocyst implant in the uterus. Blastocyst is formed by two types of cells the trophoblast cells and cell mass. Trophoblast cells are found on the outer side and form placenta while the cell mass is present on the inner side and incorporate in fetal membrane and fetus formation. Zona pellucida disrupts on the sixth day, with its disruption the blastocyst comes out and the process proceeds with the implantation of blastocyst in the uterus wall. Soon after implantation trophoblastic cells and endometrial decidual epithelia and invasion of uterine cells occur. Meanwhile, there is some protease secretion found that promotes this invasion into uterine stroma. Implantation occurs normally anterior or posterior lateral wall. When eight day arrives, trophoblastic cell differentiation occurs. They differentiate into multinucleated outer cells known as syncytiotrophoblast and inner mononucleated cells known as cytotrophoblast. The syncytiotrophoblast sends out projections that cause erosion of maternal tissues. This syncytiotrophoblastic cells also produce hCG (Hormones like Human Chorionic Gonadotropin). This hormone is produced during the second week and it a marker used for testing pregnancy. As the ninth day arrives, syncytiotrophoblast causes maternal tissue erosion allowing the invasion of maternal blood via spiral arteries of uterus. Maternal blood from these arteries enters the lacunar network. Till the end of second week uteroplacental circulation, establishment occurs. In between this time interval primary chorionic villi is being formed by the cytotrophoblast. These villi are finger like projections and they penetrate the syncytiotrophoblast. When the third week starts the growth of extraembryonic mesoderm occurs. These embryonic membranes grow into these villi and develop a loose connective tissue core. At this point, these structures are known as secondary chorionic villi. When third week proceeds towards end secondary villi transformed into tertiary villi by the formation of embryonic vessels in embryonic mesoderm. From these tertiary villi, cytotrophoblast undergoes profound growth towards decidua basalis and initiates its spreading around decidua basalis of uterus leading formation of a shell of cytotrophoblast. This shell is known as anchoring villi. These villi grow its extensions given the shape of a tree like structure. This structure is a mode of metabolite exchange between fetus and mother. The maternal spiral arteries increase their blood flow and decrease the resistance to meet up fetus’ nutrition and other requirements. Invasion of cytotrophoblast in these arteries undergo endothelial and epithelial differentiation. This differentiation increase vascular diameter as well as decrease resistance so blood flow is increased. (Speller, 2019)
Placenta is very important organ as it play a vital role in growth of fetus. It is reported from some studies performed past few years ago there is a difference in weight, total thickness and surface area of placenta based on sex. The thickness and surface area reduction is associated with decreased weight of placenta at the time of birth, but this is not related to sex they are independently associated to the weight. (Hill, 2020)
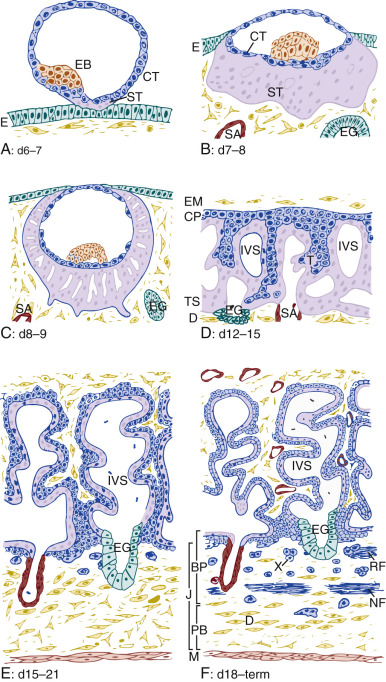
Figure 1A: Implantation, B: prelacunar period, C: beginning of lacunar period, D: primary villus stage, E: secondary villus stage and F: tertiary villus stage (Frank, 2017)
The process of implantation occur on sixth and seven day. Prelacunar period continues from seven day to eighth day at the end of this period lacunar period start from day eight till day nine and after lacunar period villus stage continue from day twelve to day fifteen then secondary villus formation occur till day twenty one and it starts from day fifteen which leads to third villus stage from day eighteen till the end which is term.
2. The function of the normal placenta.
Placenta is an important organ in maternal and fetal physiology. Due to this importance they share several responsibilities:
Implantation:
Syncytiotrophoblast which ultimately grow into placenta has an important function that it promotes the implantation via invasion into the endometrial uterine wall. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Maternal recognition of pregnancy:
These syncytiotrophoblastic cells are also involve in formation of Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) hormone. This hormone release from these cells and stimulate production of progesterone. This production of progesterone helps in maintaining the pregnancy. As due to the absence of progesterone menses will occur and the implanted zygote is sloughed. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Nutrient and gas exchange:
Villi present terminally has an important function. This important function is exchange of nutrients among mother and fetus and exchange of gases. Blood flow from mother carries oxygen, hormones, some electrolytes along with water and other nutrients. The fetus undergo exchange of carbon dioxide, water, and some waste material including urea. Although the two circulation do not come in contact directly or mix in one other but the exchange occur through passive transport or active transport. This is how nutrients exchange and exchange gases occur. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Preliminary function of placenta is baby’s development through nutrients. As pregnancy possess several complication so most of the time due to these complications the nutrient supply to fetus gets disturbed. (Mayo, 2018 )
Fetal protection from any immunologic attack:
Placenta has an ability to metabolize several substances and it also has an ability to provide anti microbial protection. This effect is obtained by the help of Macrophages which are present in chorionic villi stroma and cells of syncytiotrophoblast. These macrophages and some leukocytes provide protection to fetus. These leukocytes are present in uteral endometrium and provide help in having a successful pregnancy. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Prepare environment:
It is well known that placenta secretes hormones. Placental hormones helps in maintaining pregnancy. There is preparation of mother’s body for pregnancy. This preparation is provided by several hormones being secreted through placenta. Cardiovascular adaption is the important preparation of mother’s body for pregnancy. Growth factor of placenta promotes maturity and development of fetus. Human placental lactogenic (HPL) also known as Human chorionic somatomammotropin (HCS) undergo development of breast and metabolism will also be enhanced in mother. To enhance metabolism placenta decreases insulin sensitivity so increased amount of glucose will be available for the fetal nourishment. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Complications in formation of placenta can lead to life threatening consequences for both the mother and the baby. There is a study done on proportion of deaths occurring in UK annually. The study calculated those no. of death which occurred from placental disorders or pregnancy disorders. The ratio for these deaths id 50%. This study also find out the no. of death occurred annually in UK is 1500. Growth restriction (FGR) also known as pre eclampsia causes occurrence of complications in 40,000 pregnancies. Pre eclampsia is a condition in which mother have swelling known as edema with protein in the urine and high blood pressure. (Mayo, 2018 )
3. Placental adhesive disorder
Consequences of caesarean delivery leading to increased occurrence of invasive and abnormally adherent placentation is believed worldwide and very few doubts arise in this conception. The diagnosis of invasive and abnormally adherent placentation done on pathological basis needs to be accounted. (Sally L. Collins, 2018 )
Placenta previa
Placental implantation over the cervix is not much painless bleeding of vagina during third trimester. Non tender uterus with softness found upon examination done physically but non distressed fetus. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Placental abruption
Placental abruption is also stated as Abruption placentae. As the name indicate in this condition we simply have a partial or complete sudden separation found in placenta from the uterus. Placenta separates prematurely from decidua basalis, this separation leads to vaginal bleeding in pregnancy occurred lately. But the case in placenta previa is not same to this condition. In placenta previa uterine bleeding is painless but here the bleeding is painful with stringent contractions. One more dissimilarity in both conditions is fetus is in distress in condition of placenta previa but in this condition fetus is usually found in distress. Bleeding occur due to maternal vessels rupture, but there is a consequence of fetal placental vessels rupture that leads to separation of decidua basalis and placenta. Ultrasound is considered to be most reliable and used tool for diagnostic purposes. Such Condition has the potential to affect blood circulation among both mother and fetus, and they can lead to several risk factors which include increased blood pressure, trauma, and premature membranal rupture. Delivery of the baby is considered to be a treatment of placental abruption. This abruption had a potential to cause stillbirth. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS)
Is a condition which is known as morbidly adherent placenta, describes the improper attachment and separation of the placenta to a defective decidual layer of the endometrium. Women in maternal age possessing history of caesarean section or uterine surgery or multiparity are at increased risk for this condition. This condition was discovered via ultrasound technique, done before having a delivery in order to decrease the defective co morbidities as there is a consequence attached with this condition which is difficulty in separation of placenta after birth the separation is the cause of postpartum bleeding. Due to this severe consequence the diagnosis is crucially important to be done so that preparation for labor can be carried out, for this condition the treatment of this involve surgery for delivery. If it will not be clear by using ultrasound then we have to proceed to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) which is a more advanced technique and the diagnosis will be clearer. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Placenta Accreta
Placenta adhere abnormally in some conditions and with this adherence absence of decidua basalis is also found. This condition profoundly enhances its occurrence in women who have history cesarean section comparatively to the women without a history of surgical delivery. (Hill, 2020)
This condition known as Placenta Increta usually occurs when there is deep attachment of Placenta found into the wall of uterine leading to penetration to the muscles. This penetration will not lead to uterine serosa. At least 15 17% cases have this condition. (Hill, 2020)
Placenta Percreta
In this condition penetration of placental villi occur into uteral myometrium through serosa of maternal uterus. (Hill, 2020)
4. Ultrasound
Sonography is first imaging modality used for placental evaluation in the placental adhesive disorders. Power and coloring of Doppler techniques generate limitations. It is difficult to visualize vascularity of placenta and enable to assess feto placental and utero placental both circulations (Lamiaa Bassam Hashema, 2016)
MR imaging possess several properties in different to other techniques. These properties make them stand apart from other techniques. The techniques are suitable for placental defect detection Scanning can be done by using LOGIQ 7 PRO, GE ultrasound machine. There are two approaches that can be used one is the Trans abdominal approach which utilizes 3–5 MHz transducer. While the Trans vaginal or Tran’s labial approach utilizes 7–8 MHz endo luminal transducer. They are used for assessing the myometrium and the urinary bladder interface. This approach is helpful in case of obesity and when filling of bladder is inadequate. (Lamiaa Bassam Hashema, 2016)ultra sound is one of the advanced monographic technique it not only be considered as effective and safe but also it is reliable as it can be placed at the bedside of the patient. Ultrasound utilizes radiation for detection of morphologic diagnosis placental localization and detection of death. (Kapila & Chaudhry, 2019.)
Ultrasound diagnosis of abnormal placenta can easily be done for previously defined conditions. in predefined conditions when there will be any of the following condition is detected there is a chance of previously described placental diseases: increased loss of echo lucent area between placenta and urinary bladder or uterus, presence of placental lacunae, urinary bladder mass extension. MR prenatal pelvic images were reported by a radiologist using the afore mentioned criteria: intraplacental bands having low intensity bearing signals on images that are T2 weighted, differential signaling intensity in placenta, occurrence of placenta previa, presence of bulging of uterus, myometrial wall focal interruption, thinning of wall of myometrium up to less than 1 mm thick, urinary bladder tenting, and placental tissue invasion somewhere outside the uterus. (Philip S. Lim1, 2011, )
5. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used in the diagnosis of different placental disorders. Some Specific acquisition sequences used that are fast to detect the defects by decreasing the motional maternal and fetal misrepresentations of tissue structures. T2 weighted MR images are used as they detect accurately or more precisely when the mass is highly intensified and heterogeneous tissues present. These images are also useful in focal thinning assessment of myometrial walls and junctional zone interruption. (al., 2018) MRI was performed in the afore mentioned placental adhesive conditions by using 1.5 T medical system. The person should be imaged in supine position.
6. Difference in Ultrasound and MRI
Several studies have been done having different diagnosis of PAD with ultrasound and MRI. In some of the studies MRI findings were compared not with histologic confirmation but with surgical confirmation to have differentiation among placenta accreta, placenta increta, and placenta percreta. MRI has several important features which stands it beyond ultrasound, one of the most common feature of MRI is that it can penetrate more deeply than ultrasound so that if, in any of the case from placenta accreta, placenta increta, and placenta percreta, ultrasound is showing unclear diagnosis MRI diagnosis provide a clear imaging of the condition which leads to manage the condition and select the possibility of caesarean or normal delivery.
True positive findings of ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging MRI was found in placenta accreta, placenta increta, or placenta percreta was found upon histological examination of the uterus. But in case of true negative finding we have easy placental detachment from the decidua basalis accompanied by excessive postpartum bleeding with normal histological examination of the uterus. (Philip S. Lim1, 2011)
MRI is well known as being sensitive in detecting chronic hemorrhage and sub acute hemorrhage in several organisms because of its ability to de phase hemosiderin and iron. These two hemosiderin and iron are the cause of magnetic field inhomogeneity. They appear as foci having low signal intensity bands and decreased intensity. These bands are easy to be observed in case of high signal intensity as in case of normal placenta but in case of abnormal placenta in case of placenta accreta, placenta increta, and placenta percreta these bands are fairly not easily seen due to low intensity. MRI has the ability to detect the change in notion more fastly than ultrasound. Accreta findings has the ability to be observed 4–7 weeks earlier through MRI than through ultrasound. (Philip S. Lim1, 2011, )
Is there any finding in the case of placenta percreta in which few days prior to ultrasound placenta percreta can be identified? If there are some findings done before how much earlier a placenta percreta can be detected. This is the question which we are going to cover in this paper.
7. Works Cited
- , D. M. (2018). Placenta accreta. Retrieved from Radiopedia.
- Frank, H. G. (2017). Placenta Development. Fetal and Neonatal Physiology (Fifth Edition).
- Hill, M. (2020, April 2). Placenta Development. Embryology Placenta Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Placenta_Development
- Kapila, V., & Chaudhry, K. (2019., February 22). Physiology, Placenta. NCBI. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538332/
- Lamiaa Bassam Hashema, D. S. (2016, June). Role of MRI versus ultrasound in the assessment of placental abnormalities and diseases. The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and uclear Medicine, Volume 47(Issue 2), Pages 641 658.
- Mayo, R. P. (2018 , August 24). Advances in Human Placental Biomechanics. ELSVIER, pp. Pages 298–306. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2018.08.001
- Philip S. Lim1, M. G. (2011, , December ). Utility of Ultrasound and MRI in Prenatal Diagnosis of Placenta Accreta: A Pilot Study. American Journal of Roentgenology, Volume 197, Pages 1506 1513.
- Sally L. Collins, F. C. (2018 , February). Abnormally Adherent and Invasive Placenta: A Spectrum Disorder in Need of a Name. PMC US National Library of Medicine National Institute of Health, Volume 51(Issue 2), Pages 165–166. doi:10.1002/uog.18982
- Speller, J. (2019, June 13). Placental Development. Teach Me Physiology. Retrieved from https://teachmephysiology.com/reproductive system/pregnancy/placental development/

Essay Writing Prices