2022-07-01

INTRODUCTION:
This report consists of the three sections in which different aspects regarding biological study has been defined in the form of diagrams, comparison table and to just simply answer the questions respectively. The biological features in both human being and animals has been elaborated very precisely and defined with the help of figures also.
SECTION 1
AC 11.1: Discuss selected characteristics of living cells.
Answer: There are several different features of living cells which are; cellular organization, reproduction, metabolism, homeostasis, heredity, response to stimuli, growth and development and adoption through evolution. Comparatively, it is obvious that the use of particular stem cell selection which is linear in shape can easily permits isolations of genuine and pure populations of cell types which are precursor and producing in a multiple and mix background of cell types after unforced dissimilarity respectively (Li et al, 1998).
CELLULAR ORGANIZATION:
It consists of more complex, compound, composite, get wider and bigger, grow and enlarges in some unique and creative way.
ENERGY METABOLISM:
It comprises of breathe, nourishment, food, eat, nutrients, evacuate, exude waste and uncultivated, vitality, spirit and energy usage.
HOMEOSTASIS:
In this characteristics, the maintenance and continuation of reasonably and relatively controlled internal environment and conditions respectively.
ADAPTATION:
It consists of changes and amendments over the period of time and it is due to the natural selection, natural phenomena and mutation.
RESPONSE TO STIMULI:
In this circumstances, it acknowledges the things which is present in the external environment.
AC 11.2: Compare and Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and the impact viruses have on them.
ANSWER:
|
Prokaryotic cells |
Eukaryotic cells |
|
It consists of a single and individual chromosome which is circular |
It consists of multiple and different variety of chormosomes which is linear in shape |
|
It is a combination and binding of different kinds of architectural proteins respectively |
There are two components in eukaryotic, one is transcription and the other is translation. While, the choromosomes has found in a nucleus which is membrane bound. |
|
The transaction and translation takes place simultaneouly. |
The transaction and translation takes place in the cytoplasm. |
|
Mostly the prokaryotes consists of one copy of gene. |
While, the eukaryotes consists of two or more copy of gene. |
|
It has minimum amount of repetitive DNA. |
It has huge quantity of repetitive and non coding DNA. |
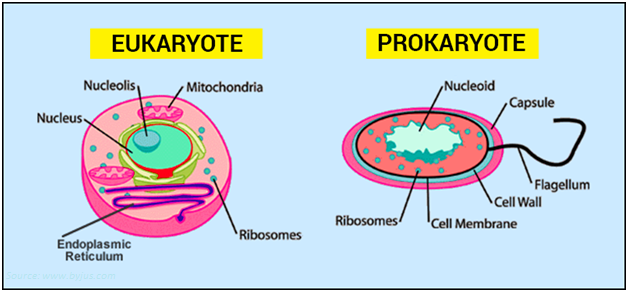
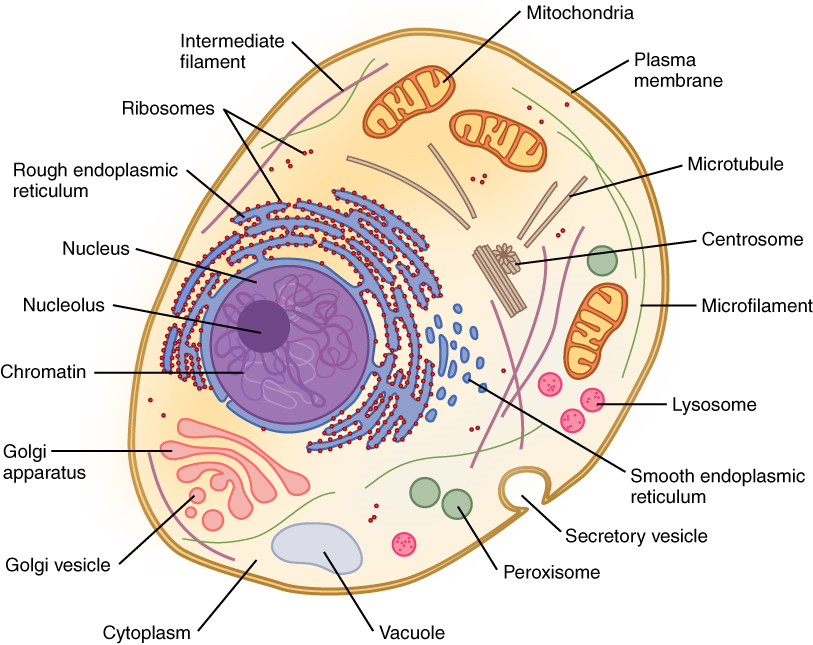
AC 11.3: Discuss eukaryotic sub cellular structure and organelles.
ANSWER: The eukaryotic sub cellular structure consists of different varieties of membrane bound organelles which are circular in shape. These assemblance and structure plays a vital and essential role in the process of common functioning of cells. They contributes from the procedure of maintaining and constructing till new biological molecules.
AC 21.1: Explain the role of the cell membrane in regulating how nutrients are gained and waste products lost.
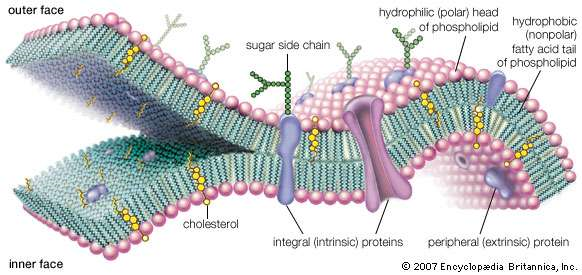
ANSWER: The main function of the cell membrane is to act as the shield or barrier among the cells and the world so in that manner, the cells wants to have structure which permits it to link with both respectively. While the cell membrane consists of a multiple layers of phospholipids whereas the cell membrane is semipermeable which permits the determined molecules just to pass in or out of the cell respectively. This appropriate mechanism and function is dependable on the movement of nutrients and the meaningful (useful) elements into the cell membrane and the elimination of waste products from the cell.
AC 21.2: Explain how animal cells use nutrients to provide the energy for growth, movement and cell division.
ANSWER: The reason behind need of food in animals is to maintain homeostasis and to produce energy. Through the combination and series of catabolic chemical reactions, The digestible carbohydrates which is present in the diet of animals are transformed to glucose molecules and then into energy respectively.
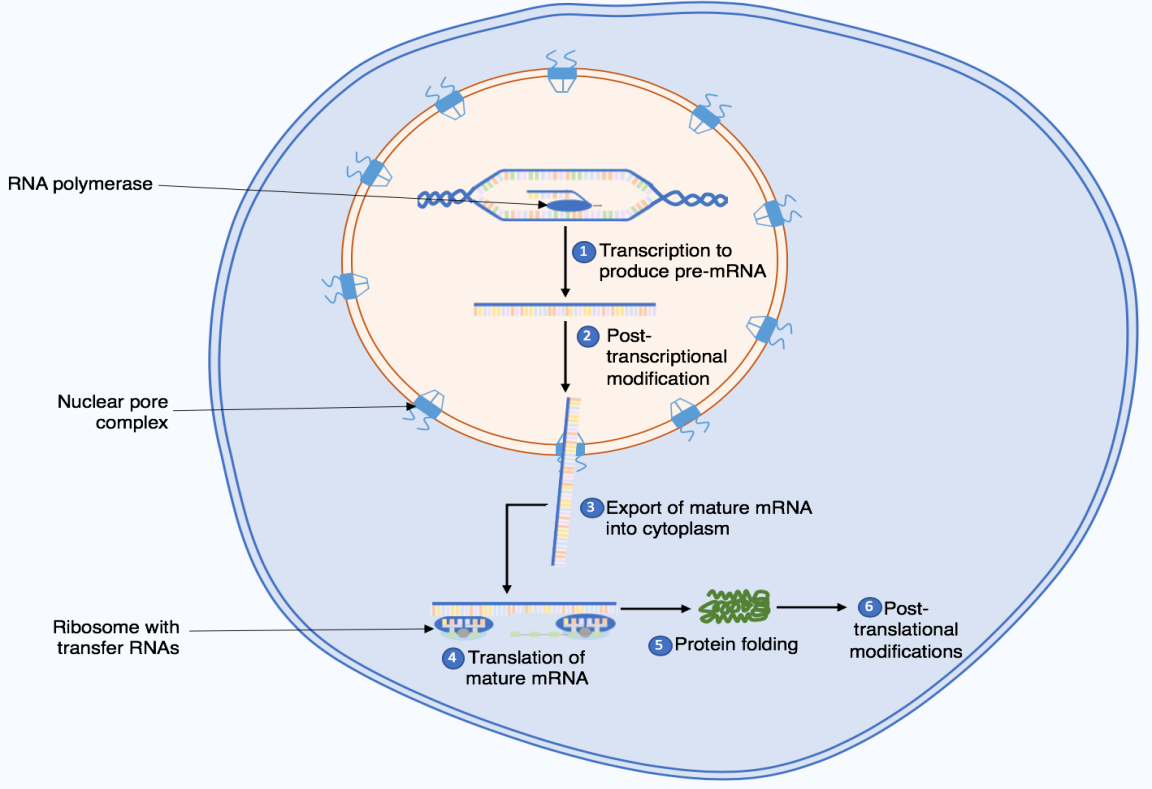
AC 21.3: Discuss the synthesis of proteins.
ANSWER: Protein Synthesis is the mechanism and procedure in which cell forms protein respectively. It contains two types of levels. One is translation and the other is transcription. Translation takes place at ribosome which comprises of proteins and rRNA.
AC 21.4: Explain the role of nucleic acids in the nucleus of cytoplasm.
ANSWER: Nucleic acids are structural unit of an element which are formulated from nucleotides that manages activities and task of cellular like protein synthesis and division of cell respectively. The messenger RNA is transported and exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm which is reproduced from the DNA and it also contains details and information for the manufacture of proteins respectively. Despite these advances, the culture and frozen storage of layer culture in the absence of LIF or MEFs, mES cells hES cells remains difficult, slow and labour intensive; also differentiate to cell types with various morphologies some cell lines require manual dissection and transfer for expressing a mixture of endoderm and mesodermal passage while bulk culture often results in non markers although no obvious mature phenotype specific differentiation. The presence of differentiated cells However, clonal progenitors of the endothelial and hemain mES cell cultures can in itself promote differentiation of topoietic lineages have been isolated more recently by any remaining stem cells; their systematic removal as new FACS from these mixed monolayer cultures and lines are established in culture increases the efficiency of under appropriate conditions, these will go on to form an their isolation. Similar approaches may substantial organised vasculature. This demonstrates that somaticly improve hES culture methods. Likewise, identification differentiation can take place in the absence of complex of the MEF derived hES differentiation inhibiting factor(s) multicellular interactions and has practical implications will represent an important breakthrough once available as since monolayer cultures are much more amenable to a culture medium supplement.
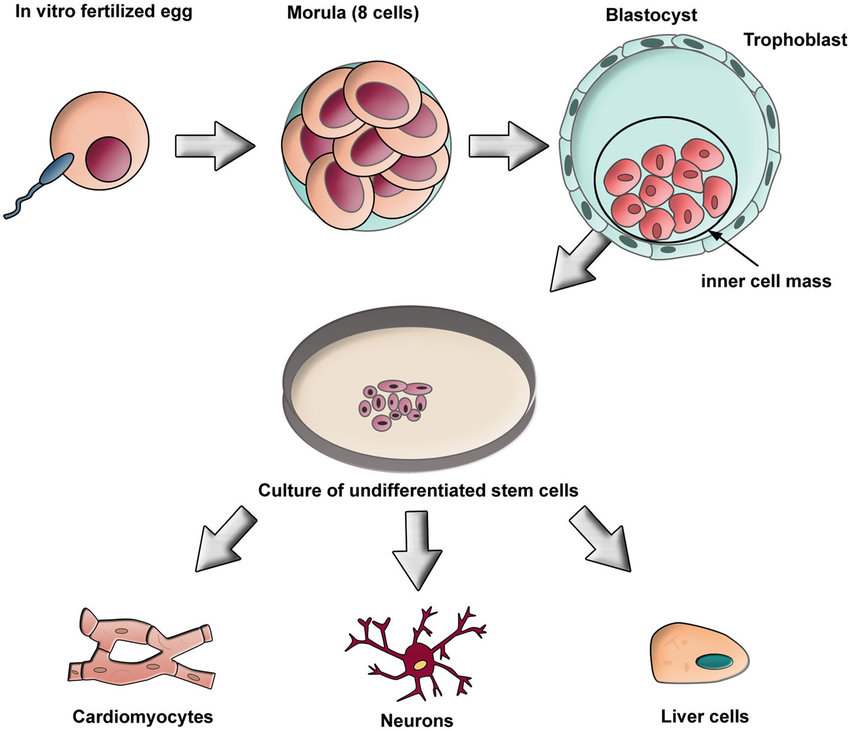
AC 31.1: Explain the generation of specialized tissues from embryonic stem cells.
ANSWER: The stem cells are those type of cells which gives the opportunity of rising multiple cell types of all tissues in the body of human being. They are generated from foetus, adult and embryo respectively. The capacity and capability is to produce dissimilarity and differentiate specific kinds of cells such as muscles and nerves. The transformation and replacement of those cells which are absent defaulted and defective tissues can produce and manage a cure. In case of some adult tissues, stem cells are required in the process of tissue repair and replacement which commonly manages and gives increase just to cell kinds which is already present in the circumambient tissues from which they are originated respectively.
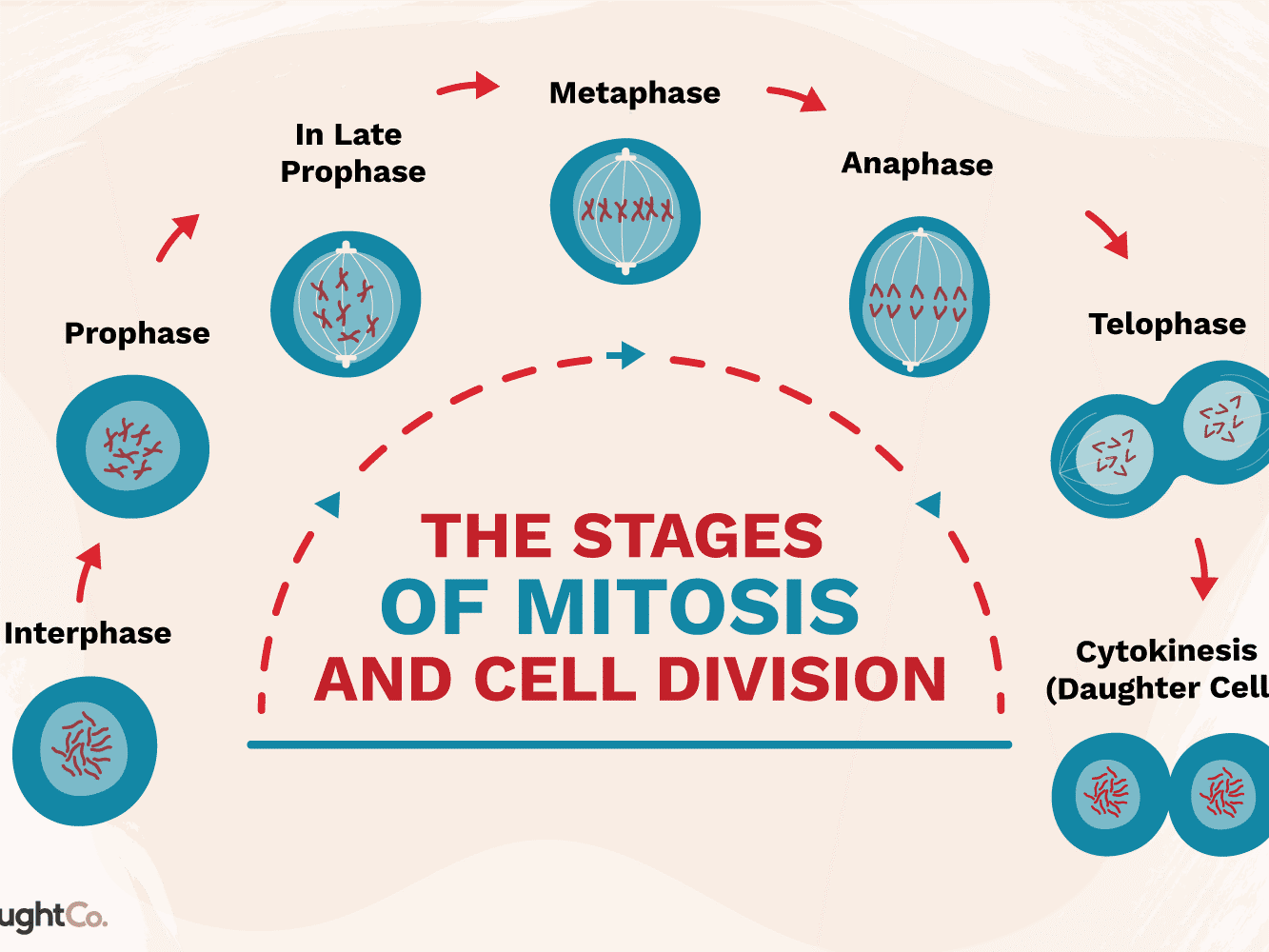
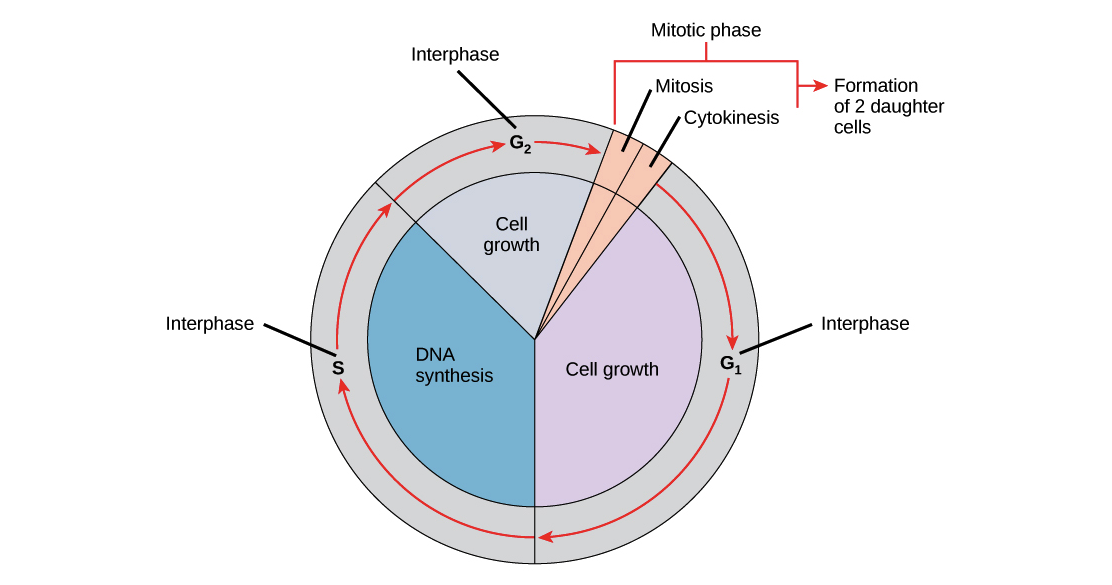
AC 31.2: Explain the importance of interphase and factors that initiate cell division.
ANSWER: IMPORTANCE OF INTERPHASE:
The mechanism and procedure of interphase in the cell cycle are that for preparation of mitosis, the cell copies its DNA during the period of interphase. The term interphase is defined as the metabolic phase of the cell in which the cell produces and maintains nutrients and proteins and metabolizes them, which help grow and conduct several other types of normal cell functions, respectively. This phase is also known as the resting place or daily living. The cell types describe and derive the dissimilarities of ectoderm into several kinds of cell lineages, respectively (Martin,1981).
FACTORS OF CELL DIVISION:
The factors of division of cell are as follows:
1) Interphase
2) Prophase
3) In Late Prophase
4) Metaphase
5) Anaphase
6) Telophase
7) Cytokinesis
AC 31.3: Explain how the same genetic information is received by each daughter cell?
ANSWER: After leaving the interphase, the cell types encounter and undergo mitosis and then formulate and complete its division. Brigid Hogan and his colleagues recorded the direct and appropriate derivation of EG cell, which is also called embryonal carcinoma from mouse primordial germ cells, respectively (Matsui et al,1992). The consequences of this procedure are produced in the form of the cell, which is known as a daughter cell, respectively. Mitosis is used to generate daughter cell, which is inherited and is similar to the parent cell. The actual work on teratocarcinomas has launched and established their origins from the cavity of germs in mice and then gave the concepts of a stem cell which is the embryonal carcinoma or it is also known as EC cell that can easily provide rise to the several types of tissues which are found in the tumors (Kleinsmith et al, 1964).
AC 31.4: Compare and Contrast cancer cells with normal cells.
ANSWER:
|
CANCER CELL |
NORMAL CELL |
|
The shape of cancer cell is irregular |
The shape of normal cell is regular |
|
The nucleus of cancer cell is darker and large |
The nucleus of normal cell is proportionate size |
|
The growth of cancer cell is out of control. |
The growth of normal cell is in control and systematic |
|
The maturation of cancer cell is immature |
The death of normal cell is mortal |
|
The cancer cell does not communicate |
The normal cell always communicates |
|
The cancer cells are invisible to immune cells |
The normal cells are visible to immune cells respectively. |
|
The cancer cells does not require oxygen |
The normal cell requires oxygen in an appropriate manner |
|
The energy efficiency of cancer cell is very low |
The energy efficiency of normal cell is very high |
|
The environment of cancer cell is acidic |
The environment of normal cell is alkaline |
THE ROLE OF THE CELL MEMBRANE IN CELLULAR METABOLISM:
There are three major functions of cell membrane regarding the regulation of nutrients in cellular metabolism:
- They usually protect the cell from toxic or poisonous substances and elements.
- They disconnect vital, but on the other hand, the mechanism and processes of incapable metabolic occurred within organelles, respectively.
- They accommodate and hold channels and receptors that permit particular molecules such as, metabolic elements and products, nutrients, proteins, wastes and ions which use to moderate and arbitrate several types of activities like extracellular and mediate cellular just for the purpose of passing among organelles, among the cell and also outside the environment respectively.
https://www.britannica.com/science/membrane biology
Many other several functions of cellular which includes the opposition and regulation of metabolic series and sequences, uptake, transformation and conversion of nutrient, synthesis and mechanism of new molecules, production and origination of energy, which occurs in the membraneous organelles respectively. Thomson and John Gearhart describes the concept and philosophy of an individual human pluripotent embryonic stem (ES) and also Embryonic germ (EG) with the help of primordial germ cell or blastocysts, respectively (Thomson et al, 1998). Hence, the cell membrane holds two main functions and mechanisms such as a type of barrier and restrict material that keeps the components and elements in and exhale the un necessary and unwanted compounds and substances out of the cell membrane, also, a gateway which permits convince and transport into the cell which is full of essential and important nutrients and proteins and movement from the cavity of waste products respectively. The advancements and developments of Embryonic mouse cells have given the philosophy of paradigm as well as much mass, which is related to the technology concerning the growth of Human Embryonic cells (Evan et al,1981).
On the other hand, the cell membrane consists of proteins, nutrients and lipids, which are based on fatty acids of primary standards and specifications. Further, there are two several kinds of membrane lipids, one is sterols, which is commonly known as cholesterol, and the other is phospholipids, respectively. While the chemical structure of the cell membrane is just like flexible, which means the main purpose is to divide and grow the boundaries of cells rapidly. But, the cell membrane is also known as a formidable barrier that permits and allows some kinds of dissolved compounds or substances just to pass the cells while blocking the rest of the cells, respectively.
In addition to this, the cell membrane takes place movements that are concerted in the duration of when the fluid substance or medium outside of the cell is internalized accurately. This process is known as endocytosis, or when the component of the internal medium of the cell is externalized, this process is known as exocytosis, respectively. This types of movement relate to the phenomena of fusion among the surfaces of membranes, which are followed by the self improvement of intact membranes. The layer of the cell is comparatively and selectively permeable towards ions and other types of organic molecules, which controls and restricts the movement of substances in and out of the cells. The main function and mechanism of the cell membrane are to protect and cover the overall cell from its surroundings, respectively. It comprises of embedded proteins and selected phospholipids bilayers appropriately.
HOW ANIMAL CELLS USE NUTRIENTS TO PROVIDE THE ENERGY FOR GROWTH, MOVEMENT AND CELL DIVISION.
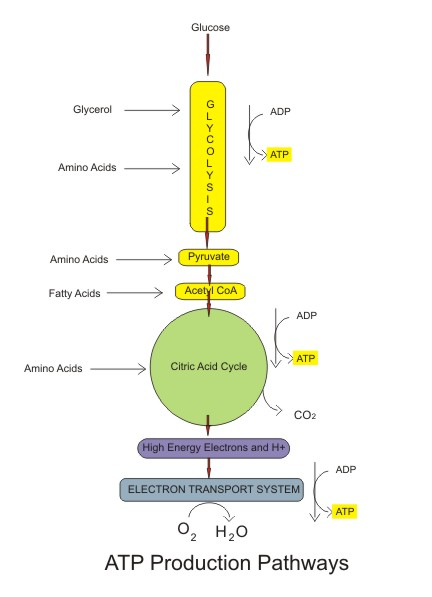
ANSWER: The cell needs a smooth and constant amount of energy contribution and supply to produce and maintain the mechanism of natural order just to keep them alive. This type of energy is originated from the power which is made up of chemical bond in food molecules, respectively. It also considers as the fuel for the cell membranes. On the other hand, Sugar is one of the essential, beneficial and important fuel molecules and further, they are catabolized in tiny and small steps and components of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Hydrogen (water). In addition to this, it controls and commands energy production in most cases of animal cells, respectively.
Moreover, a very homogeneous and related pathway also deals and operates in fungi, plants and many types of bacteria. While, the other kinds of molecules such as proteins, nutrients and fatty acids can also provide and obeys as sources of energy, respectively.
The food molecules such as fats, carbohydrates and sugars, give the main and beneficial sources of energy for most of the non photosynthetic organisms, including animals as well as human beings, respectively.
The nutrients and proteins process in order to achieve and provide sources of energy for the activities of metabolic such as movement and growth. For this purpose, glucose is a by product that collapses and breaks down to enter kerbs cycle and glycolysis just to carry out the respiration, respectively. Glycolysis is the most important pathway of ATP producing, and ATP is used to supply and provide energy for all types of reactions so that the cells which have been founded in animals can move and grow in an appropriate manner, respectively.
THE ROLE OF NUCLEIC ACIDS IN THE NUCLEUS AND CYTOPLASM.
ANSWER: Nucleic acids are those types of molecules that manage and directs activities of cellular like protein and nutrients synthesis along with the division of cell, and they are made up of nucleotides. The messenger RNA, which is also termed as mRNA is transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and it is copied from the DNA, respectively. Moreover, they contain data and information for the manufacture of proteins and nutrients during the process of mitosis, which further attacks amendments that happen in different types of stages of nuclear RNA and cytoplasmic, respectively, whereas the DNA is incorporated in organelles as well as in chromosomes. On the other hand, the DNA synthesis leads up to there dissimilarities of these organelles in both the mitochondria and plastid mechanisms and processes, in addition to this, in chromosomes happens in two several types of peaks. The nucleic acid is a type of chemical compound that is capable of being disparate to yield a mixture of organic bases compounds such as pyrimidines and purines, sugars and phosphoric acids, respectively. The main purpose of nucleic acid is to carrying information regarding cellular membranes and also by controlling the mechanism and processes of protein synthesis.
Moreover, they investigate the characteristics and features (inherited) of every living thing, including human beings and animals also. There are two several types of nucleic classes, which are ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), respectively. Whereas the function of DNA is to inaugurate the material which belongs to genetic in all living organisms while RNA is the genetic substance of particular viruses.
THIS SECTION ALSO REQUIRES YOU TO DISCUSS THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS.
ANSWER: The synthesis of protein is also called the translation. The translation presents in the cytoplasm where the ribosomes are located and placed. The structure of ribosomes is large and small types of subunits and components that are adjoining the mRNA, respectively. The synthesis of proteins indicates and symbolizes the several different kinds of biochemical processes that are responsible for the mechanism and means of amino acids as well as protein synthesis. Some levels are found in protein synthesis, such as post translational modification, transcription and translation, respectively. During the process of transcription, RNA polymerase renders and converts a coding type of area or region of the DNA which is present in the cell, and then it is generating and producing the series and sequences of RNA, respectively.
On the other hand, protein anabolism is the type of mechanism in which protein is generated from amino acids. It further depends upon several categories of processes such as translation, protein folding, amino acid synthesis, transcription and post translational modifications. The responsibility of DNA is to transform the cell, which is also known as cell’s phenotype (Hersney et al, 1953).
SECTION 3:
THE GENERATION OF SPECIALISED TISSUES FROM EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS.
ANSWER: The embryonic cell grows and develops with the help of totipotent stem cells, and they are forerunner to the basic, main and fundamental layers of tissues of the embryo, which are further categorized as pluripotent respectively. On the other hand, oligopotent stem cell is restricted to generating and becoming the most different types of cells among all the other cell types. The multipotent cells can flatter the further cells of oligopotent. The embryonic stem cells are those types of cells that can grow concerning all three layers of primary gems such as mesoderm, ectoderm and endoderm, respectively.
Regarding the body of an adult, it can form and develop into each of the more than two hundred different kinds of cells. In addition to this, the Embryonic stem cells consist of two several types of characteristics; one is pluripotency while the other is the capability and ability to reproduce separately. The pluripotency differentiates embryonic stem cells from the stem cells of an adult, which are present in the adult body in such a way that the embryonic stem cells can easily produce all types of cells in the adult body. Also, adult stem cells are multipotent and can generate just a limited number of cell types, respectively.
Moreover, Mouse embryonic stem cells are originated cardiomyocytes, which have been relocated to the heart for survival. So, there are three types of reports of the transformation of human embryonic stem cell derivates to the models of a rodent; the two stories elaborate and defines the derivation of neural progenitors from human embryonic stem cells by using the variety and combination of FGF and high cell density. Also, it can relocate to the brains of neonatal mice and the third report presents and describes the seeding of human embryonic endothelial cells.
THE PROCESS OF INTERPHASE AND FACTORS THAT INITIATE CELL DIVISION, AND THEIR IMPORTANCE.
For the division of the cell, the cell should complete some essential activities such as it should grow, break down into two daughter cells physically and copy and represent its genetic material, which is DNA, respectively. Most commonly, cell use to show and perform these activities in an appropriate manner, organized sequence and series of steps or levels which originates the makeup of the cell cycle. The cycle of the cell is defined as the cycle, which consists of a linear pathway just because from the beginning, the two daughter cells can initiate at the same time and duration at the end of each particular go round, respectively. According to the cell division, the cell consists of two different phases or factors, such as interphase and mitotic phase.
While the process and mechanism of interphase are such that it comprises of three several types of steps which are mentioned below:
1) G1 PHASE:
In the G1 phase, the cell generates and produces the molecular building blocks, the battery also grows physically larger and copies organelles, respectively.
2) S PHASE:
In this type, it copies the structure, which is microtubule organizing, and it is called the centrosome. Also, with this, the cell synthesizes an appropriate duplicate of the DNA in its nucleus, respectively. The centrosomes guide and help DNA during M phase. The DNA does not consist of any protein and nutrient, and it was not affected by the strategy or mechanism of proteases (Avary et al., 1944).
3) G2 PHASE:
The cell used to make proteins and nutrients during the second gap phase, which is G2 phase, also, the cell grows more, and it starts to restructure its opposition and content just for mitosis preparation, respectively. Moreover, when the mitosis begins, then the second phase, which is G2 phase ends appropriately.
HOW THE SAME GENETIC INFORMATION IS RECEIVED BY EACH DAUGHTER CELL.
ANSWER: Just because in the copied chromosomes, the genes accommodated use to relocate to each specific and successive generation and opposition of cellular organisms, all the mitotic progeny are hereditary same. Different types of factors such as disease generating, dead and virulent exertions of Pneumococcus were capable of transfer and relocated safe, non toxic and harmless cells of non virulent Pneumococcus into harmful organisms respectively (Griffiths,1929). The scientists declare that these chromosomes are hyper replicated, which permits for the copious manufacture and production of different types of proteins and nutrients that guide and help to produce larval metamorphosis and growth (Gilbert,2008).
THIS SECTION ALSO REQUIRES YOU TO COMPARE AND CONTRAST CANCER CELLS WITH NORMAL CELLS.
|
CANCER CELL |
NORMAL CELL |
|
The shape of cancer cell is irregular |
The shape of normal cell is regular |
|
The nucleus of cancer cell is darker and large |
The nucleus of normal cell is proportionate size |
|
The growth of cancer cell is out of control. |
The growth of normal cell is in control and systematic |
|
The maturation of cancer cell is immature |
The death of normal cell is mortal |
|
The cancer cell does not communicate |
The normal cell always communicates |
|
The cancer cells are invisible to immune cells |
The normal cells are visible to immune cells respectively. |
|
The cancer cells does not require oxygen |
The normal cell requires oxygen in an appropriate manner |
|
The energy efficiency of cancer cell is very low |
The energy efficiency of normal cell is very high |
|
The environment of cancer cell is acidic |
The environment of normal cell is alkaline |
REFERENCES/ BIBLIOGRAPHY:
1) Gilbert, 2. (2008). Although mitosis and meiosis both involve cell division, they transmit genetic material in very different ways. What happens when either of these processes goes awry?. Mitosis, Meiosis, And Inheritance, 1(1), 206.
2) Griffiths, 1. (2020). The structure and functions of nucleic acids (pp. 1 70). Bolton: C.F.A Bryce.
3) Avary et al,1., (2020). The structure and functions of nucleic acids (pp. 1 70). Bolton: C.F.A Bryce.
4) Hersney et al., 1. (2020). The structure and functions of nucleic acids (pp. 1 70). Bolton: C.F.A Bryce.
5) Thomson et al, 1. (1999). Human embryonic stem cells. Journal Of Cell Science, 113, 5 10.
6) Evan et al,1. (1999). Human embryonic stem cells. Journal Of Cell Science, 113, 5 10.
7) Kleinsmith et al,1. (1999). Human embryonic stem cells. Journal Of Cell Science, 113, 5 10.
8) Matsui et al,1. (1999). Human embryonic stem cells. Journal Of Cell Science, 113, 5 10.
9) Martin,1. (1999). Human embryonic stem cells. Journal Of Cell Science, 113, 5 10.
10) Li et al,1. (1999). Human embryonic stem cells. Journal Of Cell Science, 113, 5 10.

Essay Writing Prices